IBDP Economics SL – Microeconomics – Role of government in microeconomic -Paper 2 Exam Style Practice Questions
Role of government in microeconomic Paper 2?
Exam Style Questions..
Subject Guide IBDP Economic IBO
IBDP Economic SL- All Topics
Exam Style Question for Role of government in microeconomic -Paper 2
South Africa’s grain millers oppose corn tariff
- A battle is taking place between South African corn farmers and the corn millers who process corn. Grain South Africa (Grain SA) is the organization that represents the interests of corn farmers. It has asked the country’s International Trade Administration Commission (ITAC) to protect local corn farmers from low global corn prices by imposing a tariff on corn imports.
- South Africa’s corn millers are opposing the request by Grain SA to implement the tariff on corn imports. The corn millers argue that a tariff will cause a burden for consumers and cattle farmers. In South Africa, corn is an essential food and also a source of feed for livestock.
- According to Reuters news service, South Africa is “Africa’s largest corn producer and is relied upon by neighboring Sub-Saharan nations to [reinforce] their own corn supplies and feed their people.” A drought in South Africa has dramatically increased the price of corn. In addition, the reduced supply has prompted the need for imports. “South Africa [has traditionally been] a net exporter of corn … [but] for the second year in a row, [the economy] will become a net importer of corn.” The need to import corn has shocked both the corn farmers and the government.
- The United States (US) is the world’s largest corn producer. An unusually large harvest has increased US supply and more than halved the price of US corn to its current price of US$145 a ton. However, in South Africa, because of the drought, prices for domestically produced corn have more than doubled to reach an all-time high of US$348 a ton. The low import prices of US corn have made it very difficult for South African corn farmers to earn sufficient income to survive the drought, which is why they have asked ITAC for protection.
- However, a spokesperson for the corn millers said “we are strongly opposed to any attempt to apply a tariff. Why do we need protection for a commodity in which we are so self-sufficient?” However, Grain SA have claimed that corn farmers cannot compete with the big corn-exporting countries, such as the US and Mexico, because their governments are subsidizing corn farmers. According to Grain SA, South African farmers get almost no assistance. This is why they have requested that ITAC implement the tariff to protect corn farmers from these unfair trade practices.
- According to economists, South Africa will probably need to import about 970 000 tons of corn this year and a further 3.8 million tons in the following 12 months. To make matters worse, the rand (South Africa’s currency) has experienced a sharp depreciation against the US dollar. Combined, the need to import corn and the depreciation are likely to negatively impact South Africa’s current account
Question
▶️Answer/Explanation
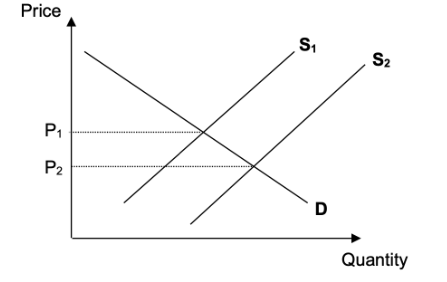
Using a demand and supply diagram, explain the effect of government subsidies on the US corn market (paragraph [5]).
For drawing a D&S diagram showing a shift of supply to the right, with a decrease in price and an increase in quantity and an explanation that a subsidy will cause a decrease in the costs of production of US corn farmers, therefore leading to an increase in supply, resulting in a lower price and an increased quantity.
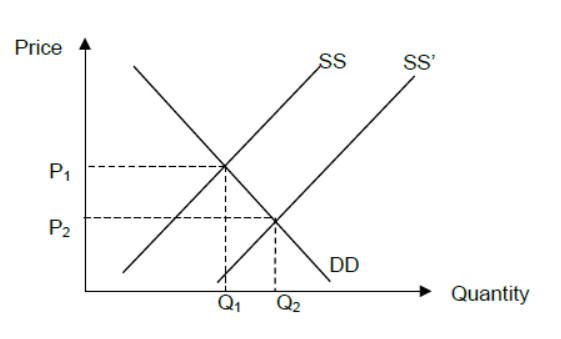
Question
Using a demand and supply diagram, explain how government subsidies may help to keep food prices low (Text E, paragraph 4).
▶️Answer/Explanation
For a demand and supply diagram showing a shift of the supply curve to the right and a fall in price AND an explanation that government subsidies may help reduce (the farmers’) cost of production and hence lead to greater supply and lower prices.