IBDP Economics HL – Macroeconomics – Measuring economic activity and illustrating its variations -Paper 2 Exam Style Practice Questions
Measuring economic activity and illustrating its variations Paper 2?
Exam Style Questions..
Subject Guide IBDP Economic IBO
IBDP Economic SL- All Topics
Exam Style Question for IBDP Economics HL- Measuring economic activity and illustrating its variations -Paper 2
Economic development in two West African countries
Ghana
- Ghana is the world’s second largest cocoa producer and Africa’s second largest gold producer. It is one of Africa’s fastest growing economies and has made major progress in achieving persistent economic growth.
- Over the last decade, Ghana has enjoyed increasingly stable and improving democratic governance. Four successful elections during the decade have strengthened the effectiveness of key national institutions, improved investor confidence and created an environment that promotes investment and growth.
- Ghana enjoys a high degree of media freedom; the private press and broadcasters operate without significant restrictions. The media are free to criticize the authorities without fear of punishment, says the non governmental organization (NGO) Reporters Without Borders. The private press is allowed to express criticism of government policy, which increases the accountability and transparency of the government.
- Although Ghana’s growth has been fairly strong, the source of growth has always been dominated by commodities and the capital-intensive services sector. Neither of these has a direct effect on poverty reduction. Growth in rural areas is often limited by basic infrastructure, such as roads. This limits the ability of people in rural areas to access markets in urban areas.
Nigeria - Nigeria is Africa’s leading oil producer. In 2016, it experienced its first full year of recession in 25 years. Global oil prices reached a 13-year low and oil production was drastically cut. Oil has continued to dominate Nigeria’s growth pattern, but the volatility of oil-dependent growth prevents progress in social and economic development.
- On the political front, the transition from military dictatorship to democratic rule has been acclaimed as one of Nigeria’s major successes in the last decade. The 2011 general election, supported by the United Nations, was widely acknowledged by international observers and domestic monitors as one of the freest and fairest elections conducted in the country in recent years.
Ghana and Nigeria - Both Ghana and Nigeria have cut fuel subsidies in order to reduce their budget deficits. This has had severe consequences for low-income households.
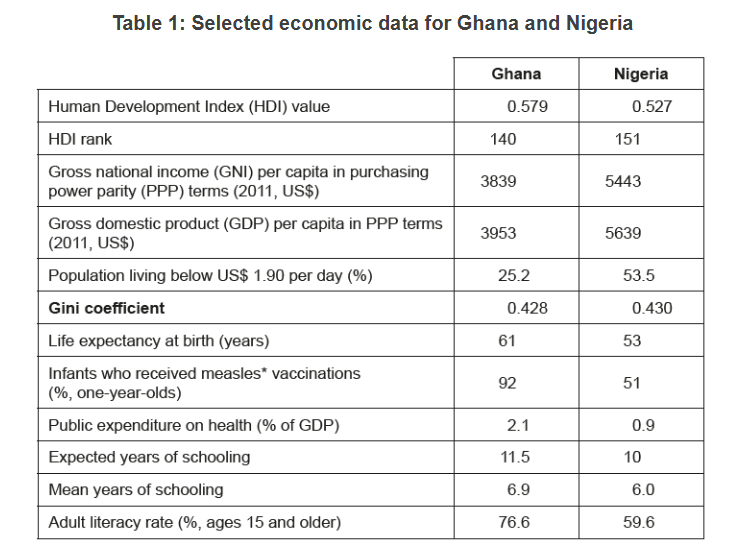
Question
State the reason for the difference between Ghana’s GNI per capita and its GDP per capita (Table 1).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Can the Democratic Republic of the Congo achieve its economic potential?
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is a nation of great potential. It has large mineral resources and an abundance of fertile land. The mining and export of cobalt, copper and gold are the main source of government revenue. However, the abundance of natural resources causes devastating conflicts as rebel groups fight for control of the DRC’s resources. With a population of 80 million and gross domestic product (GDP) per capita of only US$457, the DRC is one of the world’s poorest nations. It is ranked 176 in the world in terms of the Human Development Index (HDI).
- The government has been accused of relying too much on tariffs, but to improve living standards, the government needs revenue to spend on agriculture, electricity and roads. Furthermore, business owners in the DRC complain of corruption and increasing “red tape” (excessive regulations).
- The government believes that a strong agricultural sector could boost economic growth but only 10 % of the land is used for farming. Rice, maize and other crops grow well in the tropical climate and yet the government spends US$1 billion per year importing basic foods. According to a government spokesperson, the lack of infrastructure is a major barrier to the processing and transporting of agricultural products. The DRC’s road network is so bad that farmers and traders often make a two-week trip in small boats down the Congo River to sell their produce. The DRC has just 27 877 kilometres (km) of roads. It is estimated that 90 000 km of national roads and 150 000 km of rural roads must be built.
- In addition, the World Bank reports that only 17 % of the DRC’s population has access to electricity, despite the capacity of the Congo River to generate enough electricity to satisfy the needs of the region.
- To make matters worse, the regional conflicts have affected the availability of healthcare services. It is estimated that half of the health centres have been looted*, burnt or destroyed. Government expenditure on healthcare per capita remains one of the lowest in the world. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are relied on to protect the health and wellbeing of citizens. NGOs help to achieve this by distributing medicine and teaching families about hygiene and proper sanitation.
Question
Define the term gross domestic product (GDP) per capita indicated in bold in the text (paragraph [1]).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Economic development in Honduras and Guatemala
Honduras
- Honduras is a developing country in Central America. While historically dependent on the export of primary products, Honduras has more recently diversified its exports to include clothing and automobile components. Honduras’ economy depends heavily on exports to the United States (US) and, to a lesser extent, on remittances (money sent by a foreign worker to their home country).
- In rural areas, approximately one out of five Hondurans lives in absolute poverty. The country is also vulnerable to external shocks and has experienced worsening terms of trade. Revenue earned by the agricultural sector has decreased by one-third over the past two decades. This is partially due to the declining prices of the country’s export crops, especially bananas and coffee beans.
- The Dominican Republic-Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) has helped attract foreign direct investment (FDI). However, a threat to future FDI inflows is Honduras’ high level of crime and violence. It has one of the highest murder rates in the world.
Guatemala - Guatemala shares a border with Honduras. Guatemala has the largest population and the biggest economy in Central America. Guatemala is the top remittance recipient in Central America as a result of large numbers of Guatemalans living and working in the US. These inflows on the current account are equivalent to two-thirds of the country’s export revenue and about 10 % of its gross domestic product (GDP).
- The agricultural sector employs 31 % of Guatemala’s labour force. Key agricultural exports include sugar, coffee, bananas and vegetables. The CAFTA-DR has reduced the barriers to FDI, resulting in increased investment and diversification of exports, particularly in iron, steel and non-traditional agricultural exports (such as high-priced fruits and vegetables). While the free trade agreement has improved the conditions for investment, FDI continues to be limited by concerns over security, the lack of skilled workers and poor infrastructure.
- With some of the worst poverty, malnutrition and infant mortality rates in the region, Guatemala’s economic development is slowing. Those worst affected live in rural areas. Faster economic growth is crucial to achieving the country’s medium- and long-term poverty reduction objectives.
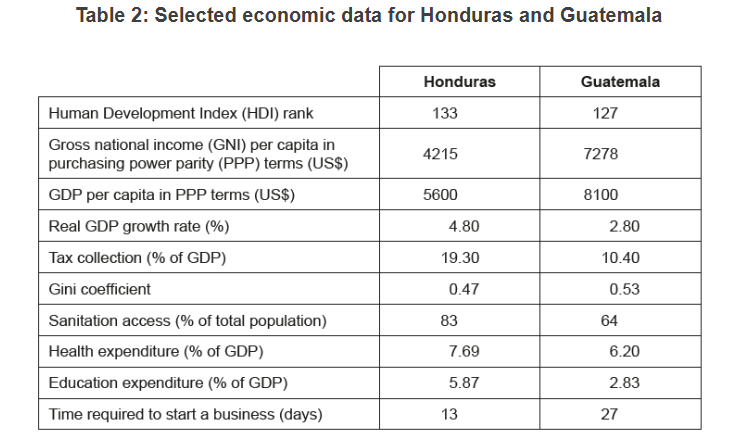
Question
With reference to the data in Table 2, explain why the GNI per capita for Guatemala is lower than its GDP per capita.
▶️Answer/Explanation
GNI is income from productive factors owned by residents of the country whereas GDP is income produced in the country
GNI per capita in Guatemala at 7278 is lower than the GDP per capita at 8100.
foreign owners of productive resources in Guatemala are earning more income than owners from Guatemala are earning in foreign countries.
The strong Thai baht
- Thailand’s currency, the Thai baht, ended 2019 at its highest value in more than six years. With a 7.8 % gain against the United States dollar (US\($\)), it was the currency that appreciated the most among major Asian currencies.
- The Thai baht’s appreciation was caused by several factors. Many foreign investors are attracted by Thailand’s economic stability, high levels of foreign reserves, low inflation rate and low unemployment (Table 1). However, the inflation rate is below the central bank’s target.
- Initially, the central bank of Thailand (BoT) was not too concerned, as the strong Thai baht was helping Thai importers and those who had foreign debts. Additionally, Thai producers could afford to import new technology and capital equipment. An appreciating currency could also help improve the country’s terms of trade.
- However, a strong currency can have severe consequences on an export-oriented country like Thailand. Exports account for 65 % of gross domestic product (GDP), and in 2019 exports declined by 7 %. Additionally, the tourism industry, which makes up approximately 20 % of GDP and accounts for 16 % of employment, started to express concern. Economic growth in 2019 was 3 %, down from 4.1 % in 2018.
- Therefore, towards the end of 2019, the BoT implemented measures to prevent further appreciation of the Thai baht. The BoT reduced controls on capital outflows to make it easier for Thai citizens to move money abroad. Additionally, restrictions were placed on the amount of money foreigners could hold in Thai bank accounts.
- The BoT is considering further measures including the use of foreign reserves, a decrease in the interest rate, and imposing controls on capital inflows, to prevent speculative inflows. However, these controls may impact the country’s credibility and financial markets. Expansionary monetary policy may also increase household debt which, at 78.6 % of GDP, is among the highest in Asia.
- The BoT is concerned about using foreign reserves, as this may result in Thailand being labelled a currency manipulator* by the US. Currently, Thailand’s overall large current account surplus is the only requirement it meets to be labelled a currency manipulator. However, Thailand’s bilateral trade surplus with the US is currently US\($\)19 billion, which means it is close to meeting a second requirement. Thailand wants to avoid being labelled a currency manipulator as the US may use trade protection in retaliation.

Question
Define the term gross domestic product indicated in bold in the text (paragraph [4]).
▶️Answer/Explanation
OR
An understanding that it is the sum of consumption, investment, government spending and net exports.
New policies for Brazil
- From 2010 to 2014, Brazil experienced an economic boom with annual gross domestic product (GDP) growth of 8 %. During this time, the government spent heavily on social programmes (including cash transfers and pensions) that helped millions to get out of the poverty cycle. The poverty rate decreased from 22 % to 9 % and the Gini coefficient dropped from 0.581 to 0.515. However, the spending on social programmes resulted in fiscal deficits and a large public debt, which is currently 80 % of GDP.
- In 2015, Brazil entered a recession that lasted until 2017. During the recession GDP declined by an average of 3 % per year. By 2017, the number of Brazilians living in absolute poverty climbed by 13 %, inequality worsened, and unemployment was 12 %. From late 2017 to 2019, Brazil struggled to recover, with only approximately 1 % annual economic growth.
- Some economists blamed the slow recovery on the lack of investment in education and technology during the economic boom. According to those economists, investment in human and physical capital was necessary to improve productivity and decrease the reliance on the production of primary commodities. Historically, spending on education has not been effective in reaching the very poor.
- In 2018, a newly elected government, aiming to stimulate economic growth, introduced market-oriented policies. Since Brazil has a large economy, the new government believed that Brazil should take advantage of world trade and foreign investment to boost economic growth and achieve economic development.
- The new government aimed to increase the number of multinational corporations (MNCs) investing in Brazil through deregulation and trade liberalization. Furthermore, in 2020 several state-owned enterprises were privatized.
- Additionally, new labour market and tax reforms were introduced to create jobs, increase labour force participation and make it easier for firms to hire and fire workers. The reforms included increasing the retirement age and reducing transfer payments. However, trade unions claim that the reforms are unfair and will lead to the exploitation of workers.
- There is concern that deregulation, privatization and market liberalization will put pressure on Brazil’s environment, threaten sustainable development, and benefit only urban areas. In 2017, the government introduced “green GDP” as an official measure and committed to environmental protection goals. This is necessary because, for example, over 40 % of the population live in areas without access to a sewage system and manufacturing companies are dumping untreated wastewater in rivers, contributing to water pollution.
Question
Using a business cycle diagram from 2010 to 2019, explain how cyclical unemployment may have changed during the economic boom (paragraph [1]) and the recession (paragraph [2]) in Brazil.
▶️Answer/Explanation
For explaining that during the economic boom there is an increase in GDP/output/AD therefore cyclical unemployment should fall and during the recession there is a decrease in GDP/output/AD therefore cyclical unemployment should increase.
Text D — Overview of Lebanon
- Lebanon is in the Middle East, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, and is home to nearly 7 million people. Lebanon is in an economic crisis, facing a recession, huge government debt and rising income inequality, poverty and inflation. Corruption and poor governance have been blamed for misallocation of funds that has led to low levels of investment and extensive capital flight. Additionally, Lebanon has one of the most unequal distributions of wealth in the world. In 2019, the top 10% of income earners owned over 70% of personal wealth in Lebanon.
- Infrastructure in Lebanon is poor, water and sewerage systems are basic, and roads are inadequate. Electricity supply is unreliable with people going without power for much of the day. In 2020, major buildings including food storage buildings, schools and hospitals were damaged in Beirut (the capital city of Lebanon). This was concerning as 85% of the country’s food arrives through Beirut. Fortunately, humanitarian aid was given by the international community to help rebuild the damaged buildings.
- Despite a history of inflows from luxury tourism and remittances (money sent by a foreign worker to their home country), there is a persistent current account deficit. To help with this, the Lebanese central bank has used high interest rates to attract financial inflows. Additionally, the government has borrowed funds from overseas. However, the misuse of these funds and overspending have contributed to one of the highest foreign debts in the world. Lebanon recently defaulted on foreign debt repayments worth 1.2 billion euros, which damaged its international credit rating, making it difficult to access loans needed to help solve its current economic problems.
Text E — Further challenges facing Lebanon
- Social unrest is prevalent and intensified when the government suggested raising revenue by imposing an indirect tax on social media applications such as WhatsApp. As the government struggles to pay its debts, people are concerned that subsidies on necessities such as wheat, medicine and fuel will be removed.
- Mismanagement of the state-run electricity and telecommunications sectors has resulted in unreliable services and high telecommunication prices. The state-run monopoly firms make losses, and the electricity sector relies heavily on government subsidies, putting pressure on the budget deficit.
- Lebanon currently has a managed exchange rate system with the Lebanese pound (Lebanon’s currency) linked to the US dollar (US$). However, the government is finding it difficult to maintain the exchange rate at the desired level due to insufficient reserve assets. Recent falling remittances, low levels of exports and lack of foreign direct investment (FDI) are placing downward pressure on the Lebanese pound. Lebanon has limited natural resources and a small manufacturing industry, thus relies heavily on imports. As a consequence, the gradual depreciation of the Lebanese pound has led to cost-push inflation.
Text F — Reforms and strategies for economic recovery
- The Lebanese government is seeking help from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to restructure the government debt and develop its infrastructure. However, loans from the IMF will require the following conditions to be met:
- procedures and processes established to ensure good governance, including enforcement of anti-corruption laws
- financial sector reforms implemented to build confidence in the banking system and laws to control capital flight
- government spending reduced and revenue increased through higher corporate, wealth and personal income taxes for high-income earners. Introduction of a tax on imported luxury goods and an increase of indirect taxes
- partially privatizing the electricity and telecommunications sectors to increase efficiency and encourage the exploration of new energy sources
- transitioning from a managed to a floating exchange rate system.
- Other organizations are offering development aid to rebuild infrastructure and support small to medium-sized businesses to develop the manufacturing sector and attract FDI. Currently, the manufacturing sector accounts for only 12.5% of gross domestic product (GDP). Some experts recommend that Lebanon decreases its reliance on food imports by developing its own food industry. However, Lebanon must commit to establishing good governance systems before aid organizations will provide their support.
- Lebanon has resisted seeking help from the IMF and other agencies in the past due to concerns about high levels of interference and imposed conditions that may conflict with their own government objectives.

Question
Using information from Table 3, calculate the 2015 gross national income for Lebanon.
▶️Answer/Explanation
GNI = GDP net income from abroad
GNI = 50 (2.42.9)
GNI = (US)\($\)49.5 billion
Text D — Overview of Malawi
- Malawi is a landlocked country in southern Africa. Its development plans contain 169 targets, based on the Sustainable Development Goals. Ineffective institutions and inequalities, however, make it difficult to reach every target. Although poverty in urban areas has declined, the level of absolute poverty has been increasing in rural areas where 85 % of the population lives. Causes of poverty include land degradation (80 % of the land is eroded or lacks nutrients), poor healthcare and rapid population growth. There is also a lack of human capital, which is often due to the difficulties that households have in obtaining loans for education or training. Approximately 75 % of households do not have access to formal banking services.
- Aid agencies are providing assistance. The World Bank’s Human Capital Project will increase investment and encourage reforms, such as promoting the education of teenage girls. In 2020, the World Bank also approved US$157 million (50 % as a loan and 50 % as a grant) for a government project. This project aims to increase sustainable land management practices and build water-related infrastructure, such as small dams and irrigation schemes.
- The government has encouraged the establishment of microfinance groups that act as rural banks. They provide some finance and guidance for programmes that introduce new types of crops and techniques in order to improve agricultural efficiency.
- Although 2019 was a difficult year due to drought, insect infestations, and a tropical cyclone, Malawi’s real gross domestic product (GDP) grew by 4.5 %. There is a large budget deficit and the amount of government debt (at approximately 60 % of GDP) is considered to be too high. Therefore, the government has announced plans to reduce its spending. Inflation had been forecast to increase to 14 % in 2020. Due to the planned contractionary fiscal policies, however, inflation may fall below 10 % from 2021 onwards.
- Export revenues account for over 30 % of GDP. Malawi aims to increase its exports of cotton, nuts, tea and sugar. Rising exports and lower fuel import prices could reduce the current account deficit. Despite the persistent trade deficit, Malawi is resisting calls for further trade protection. It has signed bilateral trade agreements with both South Africa and Zimbabwe. Tariffs are gradually being reduced, while other indirect and direct taxes are being raised.
Text E — Agricultural Production
- Approximately 80 % of the labour force is employed in agriculture, with few job opportunities available in manufacturing and services. Agricultural productivity is low for many reasons. The government promotes manufacturing industries and cultivation of crops for export by large-scale farms. However, small-scale and subsistence farmers have received little support in the past. Farmers use less fertilizer and irrigation than is typical in other countries. Only 3 % of cultivated land is irrigated, compared to the global average of 21 %. Other challenges are the inadequate road and rail links to markets and the limited availability of electricity and fuel.
- Maize is the most important staple food in Malawi. The government uses price controls when trying to ensure that maize is available at affordable prices for low-income households. However, the maximum price set by the government is often too low to persuade farmers to supply the maize or to provide them with sufficient revenue. In 2020, the maximum price was raised from 250 to 310 kwacha per kilogram. Even at the higher price, shortages remain.
- The government is planning to invest in commercial agriculture to improve productivity and promote diversification. The 2020 budget includes subsidies on fertilizer for 4.3 million small-scale farmers, which could possibly double maize output but may also pollute waterways. The support given to farmers will improve the nutrition of Malawians and stimulate the rural economy.
Text F — Tobacco Exports
Tobacco is Malawi’s major export, providing over 50 % of foreign currency earnings. Due to lower global demand and the purchasing policies of multinational tobacco firms, prices paid to farmers in Malawi are low and falling. To reduce costs, farmers resort to using child labour. Following allegations of labour exploitation, the United States has restricted tobacco imports from Malawi. There is concern that other importing countries might also impose restrictions.

Question
Using information from Table 3, calculate real GDP (at 2010 prices) in 2019 using the price deflator.